Echocardiography is a critical tool in modern cardiology, employing ultrasound technology to create dynamic images of the heart. The echocardiogram, often referred to simply as an echo, provides a detailed view of the heart's structure and function, helping healthcare professionals assess various heart conditions effectively.
Definition of Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram is a non-invasive diagnostic test that utilizes high-frequency sound waves to produce real-time images of the heart. These sound waves, emitted by a device called a transducer, bounce off the heart structures and are converted into moving pictures displayed on a monitor. This imaging technique allows for the evaluation of the heart's chambers, valves, and surrounding structures, providing invaluable information about its overall health. Different types of echocardiograms exist, including transthoracic echocardiograms (TTE), transesophageal echocardiograms (TEE), and stress echocardiograms, each serving specific diagnostic purposes.
Importance of Echocardiography in Cardiology
Echocardiography holds a pivotal role in cardiology for several reasons. First and foremost, it is a safe and non-invasive procedure, making it accessible for a wide range of patients. Unlike other imaging techniques that may involve radiation exposure, echocardiography is devoid of such risks, which is particularly beneficial for vulnerable populations, including pregnant women and children.Moreover, echocardiograms can be performed quickly, often within 30 to 60 minutes, and provide immediate results. This rapid turnaround is crucial in clinical settings where timely decision-making can significantly impact patient outcomes. Additionally, the detailed visualization of heart structures enables healthcare providers to diagnose a variety of heart conditions, monitor disease progression, and assess the effectiveness of treatments.

Overview of How Echocardiograms Aid in Diagnosing Heart Conditions
Echocardiograms serve as a cornerstone in the diagnosis of numerous heart conditions. They help identify abnormalities such as valve defects, chamber enlargement, and cardiac wall motion issues, which may indicate underlying heart disease. For instance, echocardiography is essential in diagnosing conditions like heart valve diseases (stenosis or regurgitation), cardiomyopathy (diseases of the heart muscle), and congenital heart defects present at birth.Additionally, the use of Doppler imaging during echocardiograms allows for the assessment of blood flow within the heart and major vessels. This capability is vital for detecting problems related to blood circulation, such as blockages or abnormal flow patterns that could lead to serious complications.Furthermore, echocardiograms assist in risk stratification and treatment planning. For patients with known heart disease, regular echocardiographic assessments can provide insights into the effectiveness of therapies, enabling healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans based on individual responses.In summary, the echocardiogram is an indispensable diagnostic tool in cardiology. By offering safe, real-time imaging of the heart, it enables healthcare professionals to detect and manage heart conditions effectively, ultimately improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
How Echocardiograms Work
Echocardiography operates on principles of ultrasound technology, utilizing sound waves to produce detailed images of the heart in real-time. Understanding how these sound waves interact with heart structures is key to recognizing the diagnostic power of this tool.
Principles of Ultrasound in Echocardiography
Sound Waves and Image Formation
Echocardiography begins with a transducer emitting high-frequency sound waves, which travel through the chest and bounce off different structures within the heart. As these waves return, the echocardiography machine processes them into visual data, creating a dynamic image of the heart on a monitor. This process allows for the non-invasive evaluation of the heart’s size, shape, and function.Because ultrasound waves reflect differently off tissues of varying densities, they allow echocardiograms to distinguish between blood, muscle, and valve tissue. This precision is crucial for diagnosing issues like chamber enlargement, abnormal wall motion, or structural defects.
Real-Time Imaging of Heart Structure and Function
One of the most significant advantages of echocardiography is its ability to capture real-time images. The continuous, moving visuals offer a live view of the heart at work—each heartbeat, valve movement, and change in blood flow can be observed as it happens. This capability makes it an invaluable tool for identifying functional abnormalities, such as impaired valve function or diminished heart muscle contraction, which might not be apparent on static images or tests like X-rays.
Visualization of Heart Chambers, Valves, and Blood Flow
Doppler Imaging for Blood Flow Assessment
Echocardiograms don't just show the structure of the heart; they also assess blood flow through Doppler imaging. This technique measures the speed and direction of blood flow within the heart and its associated vessels. For example, Doppler can identify abnormal blood flow patterns that could suggest valve stenosis (narrowing) or regurgitation (leakage), both of which can disrupt the heart's ability to pump efficiently.
The color Doppler feature adds a layer of visual clarity by assigning colors to blood moving toward or away from the transducer, making it easier to spot any irregularities in circulation. This is especially useful for identifying issues like congenital heart defects or blood clots.
2D vs. 3D Echocardiography
There are two primary modes of echocardiography: 2D and 3D.
2D Echocardiography: The most commonly used form, this technique generates a flat, cross-sectional image of the heart. It provides a clear view of the heart’s chambers, valves, and vessels, which helps in diagnosing structural abnormalities and heart function.
3D Echocardiography: This more advanced form adds depth and dimension, allowing for a more comprehensive view of the heart's anatomy. It is particularly valuable when assessing complex congenital heart conditions or planning surgical interventions. The enhanced visualization of heart valves, for instance, allows cardiologists to better understand malformations or the severity of valve diseases.
Just as mammography offers critical insight into breast health, echocardiography opens a similar window into the heart’s functionality, allowing for early diagnosis and better treatment outcomes. Both use non-invasive imaging to provide a clear picture, empowering patients and doctors to make informed decisions that enhance long-term health.
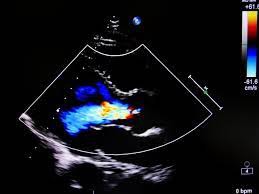
Diagnosing Heart Conditions with Echocardiograms
Echocardiograms are invaluable in diagnosing a variety of heart conditions, enabling healthcare providers to assess both the structure and function of the heart in a non-invasive manner. This section explores the common heart conditions that can be diagnosed through echocardiography and the abnormal structures that can be identified during the procedure.
Common Heart Conditions Diagnosed
Echocardiography plays a crucial role in identifying and diagnosing several prevalent heart conditions, including:
Heart Valve Disease
Heart valve disease occurs when one or more of the heart's valves do not function properly, affecting blood flow within the heart. Common types of valve diseases include:
Aortic Stenosis: Narrowing of the aortic valve, leading to restricted blood flow from the heart to the aorta. Echocardiograms can assess the severity of the stenosis and its impact on heart function.
Mitral Regurgitation: Leakage of the mitral valve, allowing blood to flow backward into the left atrium during contraction. Echocardiograms help visualize the regurgitant flow and evaluate the valve’s anatomy.
Echocardiography is essential for diagnosing the severity of these conditions and determining appropriate treatment strategies, such as medication or surgical intervention.
Heart Failure
Heart failure occurs when the heart cannot pump blood effectively, leading to insufficient blood flow to meet the body’s needs. Echocardiograms can identify the underlying causes of heart failure, such as:
Reduced Ejection Fraction: A measurement of how well the heart pumps blood. Echocardiograms help assess the left ventricular function and determine if the heart is operating at reduced capacity.
Diastolic Dysfunction: Impaired filling of the heart during the relaxation phase. Echocardiography can provide insights into the heart's ability to relax and fill properly, helping to differentiate types of heart failure.
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy refers to diseases of the heart muscle that affect its size, shape, and ability to pump blood. Common types diagnosed via echocardiography include:
Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Characterized by an enlarged heart muscle that weakens its ability to pump effectively. Echocardiograms reveal changes in the size and function of the heart chambers.
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: An abnormal thickening of the heart muscle, which can obstruct blood flow. Echocardiograms help visualize the thickness of the heart walls and assess potential obstruction.
Congenital Heart DefectsCongenital heart defects are structural problems with the heart present at birth. Echocardiograms are crucial in diagnosing various congenital defects, such as:
Septal Defects: Holes in the heart’s septum (the wall separating the left and right sides), which can lead to abnormal blood flow. Echocardiograms can identify the size and location of these defects.
Coarctation of the Aorta: A narrowing of the aorta that can lead to increased blood pressure. Echocardiography can assess the severity and impact of the narrowing on heart function.
Pericardial DiseasesPericardial diseases involve inflammation or fluid accumulation in the pericardium (the heart's outer lining). Echocardiograms help diagnose conditions such as:
Pericarditis: Inflammation of the pericardium, which may cause chest pain and other symptoms. Echocardiography can reveal signs of inflammation or fluid buildup.
Pericardial Effusion: Excess fluid accumulation around the heart, which can affect its function. Echocardiograms can measure the amount of fluid and assess its impact on cardiac performance.
Identifying Abnormal Heart StructuresEchocardiography also plays a critical role in identifying structural abnormalities within the heart, including:
Enlarged ChambersEnlarged heart chambers can indicate underlying issues such as heart failure or valve disease. Echocardiograms can measure chamber sizes, allowing healthcare providers to assess the degree of enlargement and its potential impact on heart function.
Left Atrial Enlargement: Often associated with hypertension or mitral valve disease, this condition may predispose individuals to atrial fibrillation.
Left Ventricular Hypertrophy: Thickening of the left ventricle can result from long-standing hypertension or aortic stenosis, affecting the heart’s ability to pump effectively.
Wall Motion Abnormalities
Wall motion abnormalities indicate that a portion of the heart muscle is not contracting or relaxing normally, often due to ischemia (reduced blood flow). Echocardiograms help identify these abnormalities, which can include:
Hypokinesis: Reduced motion of a heart wall segment, often seen in areas affected by inadequate blood supply.
Akinesis: Absence of movement in a segment of the heart wall, typically associated with prior myocardial infarction (heart attack).
Identifying wall motion abnormalities is crucial for determining the extent of heart damage and guiding treatment options.
Valve Function Issues
Echocardiography allows for detailed assessment of heart valve function. Abnormalities may include:
Prolapse: A condition where a valve does not close properly, leading to leakage. Echocardiograms can visualize the valve's movement and identify any prolapse.
Calcification: The buildup of calcium deposits on heart valves, which can impede function. Echocardiography can help assess the severity of calcification and its effects on blood flow.
By identifying these abnormalities, echocardiograms provide essential information for diagnosing heart conditions and guiding treatment decisions.
This detailed content outlines the common heart conditions that echocardiograms can diagnose and the specific abnormal structures that can be identified during the procedure. If you need further details or additional sections, just let me know!
Benefits of Using Echocardiograms for Diagnosis
Echocardiograms are a cornerstone in the diagnosis and management of heart conditions. They offer numerous benefits, making them a preferred choice among healthcare providers for evaluating cardiac health. This section explores the key advantages of using echocardiograms for diagnosis.
Non-invasiveness
Echocardiograms are performed externally, meaning no surgical procedures or instruments penetrate the skin.
The use of ultrasound technology eliminates the need for ionizing radiation, making it a safer alternative compared to some imaging modalities like CT scans.
Patient Comfort and Accessibility
The procedure typically involves placing a transducer on the chest with minimal discomfort.
The non-invasive nature allows for repeated use without significant risk, making it suitable for ongoing monitoring.
Ideal for Various Patient Populations
Echocardiograms can be safely used in pregnant women, children, and elderly patients who
Rapid Interpretation of Results
Results can often be available within a few hours or days, allowing for prompt diagnosis and timely treatment decisions.The ability to assess heart function in real-time facilitates quick responses to any acute cardiac conditions observed during the procedure.
Comprehensive Assessment of Cardiac Function
Detailed Visualization of Cardiac Structures
Echocardiograms provide detailed images of the heart’s chambers, valves, and blood vessels, allowing for thorough evaluation of cardiac anatomy.Advanced techniques like Doppler imaging offer insights into blood flow dynamics and valve function.
Functional Assessment
The ability to measure parameters such as ejection fraction, wall motion, and diastolic function helps in assessing overall cardiac performance.Comprehensive evaluation aids in diagnosing various heart conditions, guiding treatment, and predicting outcomes.
Cost-Effectiveness Compared to Other Imaging Modalities
Lower Costs
Echocardiograms are generally less expensive than other imaging modalities like MRI or CT scans, making them accessible to a wider range of patients.Insurance coverage for echocardiograms is often favorable, reflecting their status as a standard diagnostic tool.
Reduced Need for More Expensive Tests
The information obtained from echocardiograms can help avoid unnecessary, more invasive, or costly procedures.By providing initial assessments, echocardiograms can streamline the diagnostic process, potentially saving healthcare costs in the long run.
Ability to Guide Treatment Decisions and Management Plans
Informed Clinical Decision-Making
The detailed information provided by echocardiograms allows healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans based on individual patient needs.Providers can determine the need for medications, lifestyle changes, or surgical interventions based on echocardiographic findings.
Monitoring Treatment Efficacy
Echocardiograms can be used to track changes in cardiac function over time, allowing for adjustments to treatment plans as necessary.Regular echocardiographic assessments help evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, ensuring optimal patient care.
Facilitating Multidisciplinary Collaboration
The detailed insights from echocardiograms can facilitate collaboration between cardiologists, surgeons, and primary care providers, improving comprehensive patient management.This interdisciplinary approach enhances the overall quality of care for patients with complex heart conditions.
Conclusion
Essential Diagnostic Tool
Echocardiograms are invaluable in the assessment of various heart conditions, providing critical insights into heart structure and function.They aid in diagnosing issues such as heart valve disease, heart failure, and congenital heart defects.
Non-invasive and Effective
Being a non-invasive procedure, echocardiograms ensure patient safety while delivering accurate and timely results.heir ability to visualize real-time cardiac activity allows for early detection of abnormalities, leading to improved patient outcomes.
Guiding Treatment Decisions
The data obtained from echocardiograms supports clinicians in formulating effective treatment plans tailored to individual patient needs.
Regular use of echocardiography enhances monitoring of treatment effectiveness and the progression of heart disease.
B. Importance of Regular Cardiac Screenings
Early Detection Saves Lives
Regular echocardiographic screenings can help identify heart conditions before symptoms arise, facilitating timely intervention.
Early diagnosis correlates with better treatment outcomes and survival rates.
Monitoring Risk Factors
Regular screenings are particularly crucial for individuals with risk factors such as family history, high blood pressure, or diabetes.
Proactive management of cardiovascular health can prevent the development of more serious conditions.
Promoting Heart Health Awareness
Routine screenings encourage individuals to be more aware of their heart health and lifestyle choices, fostering a preventive approach to cardiac care.
Encouragement to Consult with Healthcare Providers for Personalized Assessments
Tailored Recommendations
Individuals should consult their healthcare providers to discuss personal risk factors and determine appropriate screening schedules based on their medical history.Healthcare professionals can provide guidance on the most suitable imaging tests, including echocardiography, based on individual circumstances.
Open Communication
Patients are encouraged to communicate any concerns or symptoms with their healthcare providers to ensure thorough evaluation and follow-up.Building a collaborative relationship with healthcare providers fosters a proactive approach to heart health management.
FAQs
A. How often should one have an echocardiogram?
Frequency of Screening
The frequency of echocardiograms depends on individual risk factors, age, and existing heart conditions. Generally, adults with no risk factors may have an echocardiogram every 5 to 10 years, while those with heart disease or risk factors may need more frequent assessments.
Are there any risks associated with echocardiograms?
Minimal Risks
Echocardiograms are considered very safe and have minimal risks. They are non-invasive and do not use ionizing radiation. Some patients may experience mild discomfort during the procedure due to pressure from the transducer, but serious complications are rare.
How should one prepare for an echocardiogram?
Preparation for an echocardiogram is minimal. Patients are typically advised to wear comfortable clothing and may be asked to avoid food or drink for a short period before the procedure, especially for transesophageal echocardiograms.
Can echocardiograms be done during pregnancy?
Yes, echocardiograms are safe during pregnancy. They do not involve radiation and can be performed to monitor the heart health of pregnant women and assess any potential issues in fetal cardiac development.
EWhat happens if an echocardiogram reveals abnormalities?
Follow-Up Actions If abnormalities are detected, the healthcare provider will discuss the findings and may recommend additional tests, such as a stress test, cardiac MRI, or CT scan, to further evaluate the condition. Treatment options will be discussed based on the specific diagnosis.
0 comments
Be the first to comment!
This post is waiting for your feedback.
Share your thoughts and join the conversation.
