Introduction to Lyme Disease
Lyme disease is a tick-borne illness caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi. It's named after Lyme, Connecticut, where it was first identified in the 1970s. This disease is now one of the most common vector-borne illnesses in the United States, affecting thousands of people each year.
Causes of Lyme Disease
The Role of Ticks
Lyme disease is primarily transmitted through the bite of infected black-legged ticks, also known as deer ticks. These tiny arachnids are commonly found in wooded and grassy areas.
Borrelia Burgdorferi Bacteria
The real culprit behind Lyme disease is the Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria. When an infected tick bites a human, the bacteria are transferred from the tick's saliva into the bloodstream.
Transmission
How Lyme Disease Spreads
Ticks become infected with Borrelia burgdorferi when they feed on infected animals, such as mice or deer. Humans can then contract the disease through tick bites. The longer the tick is attached to the skin, the higher the risk of transmission.
Common Areas for Tick Exposure
Ticks thrive in humid, wooded, or grassy environments. Areas with high deer populations are particularly prone to having large numbers of ticks. Outdoor activities like hiking, camping, or gardening can increase the risk of exposure.
Symptoms of Lyme Disease
Early Symptoms
Early signs of Lyme disease usually appear within 3 to 30 days after a tick bite. These symptoms include:
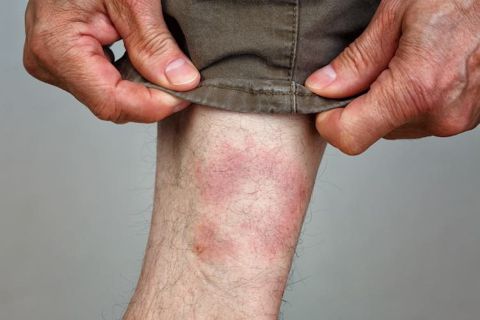
Erythema Migrans (EM) Rash: Often described as a "bull's-eye" rash, it expands gradually from the site of the bite.
Flu-like Symptoms: Fever, chills, headache, fatigue, muscle and joint aches, and swollen lymph nodes.
Later Stage Symptoms
If left untreated, Lyme disease can progress to more severe symptoms, such as:
· Severe headaches and neck stiffness
· Additional EM rashes on other areas of the body
· Arthritis with severe joint pain and swelling, particularly in the knees
· Facial palsy (loss of muscle tone or droop on one or both sides of the face)
· Heart palpitations or an irregular heartbeat (Lyme carditis)
· Episodes of dizziness or shortness of breath
· Inflammation of the brain and spinal cord
· Nerve pain, shooting pains, numbness, or tingling in the hands or feet
Diagnosis of Lyme Disease
Clinical Evaluation
Diagnosing Lyme disease begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination, focusing on any recent tick exposure and the characteristic EM rash.
Laboratory Testing
Laboratory tests from the Al-noor diagnostic center and other best labs in city, such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and Western blot tests, can help confirm the diagnosis by detecting antibodies against Borrelia burgdorferi in the blood.
Stages of Lyme Disease
Early Localized Lyme Disease
This stage occurs a few days to weeks following a tick bite, characterized by the EM rash and flu-like symptoms.
Early Disseminated Lyme Disease
This stage can occur days to months after the initial tick bite, with multiple EM rashes and more severe symptoms affecting the nervous system and heart.
Late Disseminated Lyme Disease
This stage happens months to years after the tick bite, with chronic arthritis and neurological symptoms being common.
Treatment Options
Antibiotics
The standard treatment for Lyme disease involves antibiotics such as doxycycline, amoxicillin, or cefuroxime. Early treatment is crucial for a quick recovery.
Alternative Treatments
Some patients explore alternative therapies, such as herbal treatments and supplements, though their efficacy is not well-established.
Prevention Tips
Avoiding Tick Bites
· Wear long sleeves and pants when in wooded or grassy areas.
· Use insect repellent containing DEET.
· Stay on trails and avoid tall grass.
Proper Tick Removal
If you find a tick attached to your skin, use fine-tipped tweezers to grasp it as close to the skin’s surface as possible and pull upward with steady pressure.
Living with Lyme Disease
Chronic Lyme Disease
Some patients experience long-term symptoms even after treatment, a condition often referred to as chronic Lyme disease or post-treatment Lyme disease syndrome (PTLDS).
Coping Strategies
Managing chronic Lyme disease involves a combination of medical treatment, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Impact on Daily Life
Physical Health
Lyme disease can cause persistent pain, fatigue, and neurological issues that impact daily activities.
Mental Health
Living with chronic symptoms can lead to anxiety, depression, and cognitive difficulties, necessitating mental health support.
Lyme Disease in Different Populations
Children
Children are at higher risk of tick bites due to outdoor play. Symptoms in children may include fever, headache, and a prominent rash.
Adults
Adults may experience more severe symptoms, including arthritis and neurological issues. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications.
Pets
Pets, particularly dogs, can also contract Lyme disease. Symptoms in pets include lameness, fever, and loss of appetite. Consult a veterinarian for appropriate treatment.
Lyme Disease Myths
Common Misconceptions
There are many myths surrounding Lyme disease, such as it being easily cured with short-term antibiotics or that it only occurs in certain areas.
Facts vs. Fiction
Educating yourself about Lyme disease helps debunk myths and promote better understanding and prevention.
Recent Research and Developments
Advances in Diagnosis
New diagnostic tests are being developed to improve early detection of Lyme disease, including more accurate blood tests and imaging techniques.
Potential Vaccines
Research is ongoing to develop vaccines that can prevent Lyme disease, offering hope for future prevention.
Conclusion
Lyme disease is a serious condition that can have long-term health effects if not treated promptly. Awareness, prevention, and early diagnosis are key to managing this disease effectively. By taking preventive measures and seeking early treatment, you can reduce your risk of severe complications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
FAQ 1: Can Lyme Disease be cured?
Yes, with early diagnosis and appropriate antibiotic treatment, most cases of Lyme disease can be cured.
FAQ 2: How long does it take for symptoms to appear?
Symptoms can appear within 3 to 30 days after a tick bite.
FAQ 3: Is Lyme Disease contagious?
No, Lyme disease is not contagious and cannot be transmitted from person to person.
FAQ 4: What should I do if I find a tick on my body?
Remove the tick with fine-tipped tweezers, clean the area with antiseptic, and monitor for symptoms. Consult a healthcare provider if symptoms develop.
FAQ 5: Can Lyme Disease cause long-term health problems?
Yes, if left untreated, Lyme disease can lead to chronic symptoms affecting joints, the heart, and the nervous system.
0 comments
Be the first to comment!
This post is waiting for your feedback.
Share your thoughts and join the conversation.
