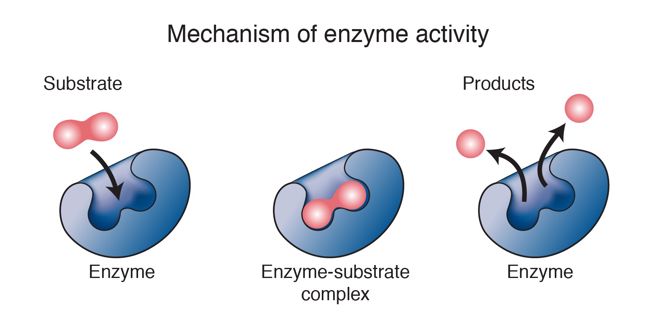
Enzyme as a function is a catalyst. It carries chemical reactions of living organisms. At normal
temperature, pH and cellular pressure, the reaction rate is high. On the basis of structure there are 1300
types of enzymes in the cell of human body. Functionally enzymes are divided into seven major groups;
oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, isomerases, lyases, ligases and translocases.
1.Oxidoreductases: These type of enzymes catalyze oxidation reduction reaction. Electrons tend to
travel from one particular molecule to the other. It depends upon substrate whether the reaction is
oxidation or reduction. Pyruvate dehydrogenase is used to catalyze the oxidation of pyruvate which is
converted into acetyl coenzyme A.
2.Transferases: Enzymes in this class help to transport the functional group among acceptors and donor
molecules. Transaminase transfers an amino group from a molecule to another.
3.Hydrolases: These are hydrolytic enzymes; catalyze hydrolysis reaction by adding water, cleave the
bond and hydrolyze it. Pepsin have the ability to break peptide bonds in protein.
4.Isomerases: Enzymes in this group catalyze structure; causing the change in shape of the molecule.
The new molecule is called isomer of parent molecule. Phosphoglucomutase converts glucose-1-
phosphate into glucose-6-phosphate.
5.Lyases: This is very strange group; they add water, CO2 or NH3 across double bond and sometimes
eliminate these products to create double bonds. These enzymes break the bond without catalysis e.g.
aldolase catalyzes fructose-1,6-bisphosphate to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone
phosphate.
6.Ligases: The ligases are known to charge the catalysis of ligation process. In this process two molecules
associate to form a complex molecule e.g. DNA ligase catalyzes two fragments of DNA, then
Phosphodiester Bond is formed.
7.Translocases: This is a new class of enzymes. It assists the molecules to move across the cell
membrane. Sometimes the movement is done to separate the ion or molecule within membrane e.g.
ornithine, carnithine etc.
Hasnain A.さんをフォローして最新の投稿をチェックしよう!
0 件のコメント
この投稿にコメントしよう!
この投稿にはまだコメントがありません。
ぜひあなたの声を聞かせてください。
